Cable Laying Roller Setup Guide for Single and Multi-Cable Projects
Author:jiujiu Release time:2026-01-12 21:13:15 Number of views:150order
Why Proper Cable Laying Roller Setup Matters
Cable installation quality depends not only on the cable itself, but also on how it is handled during laying and pulling operations. Improper guidance can result in excessive friction, surface damage, or uneven tension, especially on long or complex routes.
A Cable Laying Roller is designed to guide cables smoothly along trenches, ducts, or surface routes. Correct setup of cable laying rollers is essential for both single-cable and multi-cable projects, ensuring efficiency, safety, and long-term cable performance.
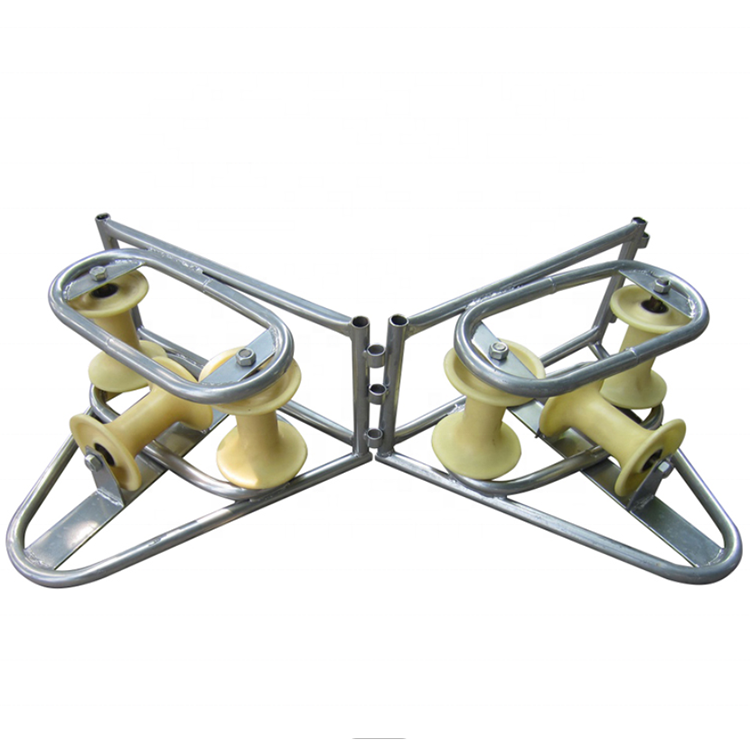
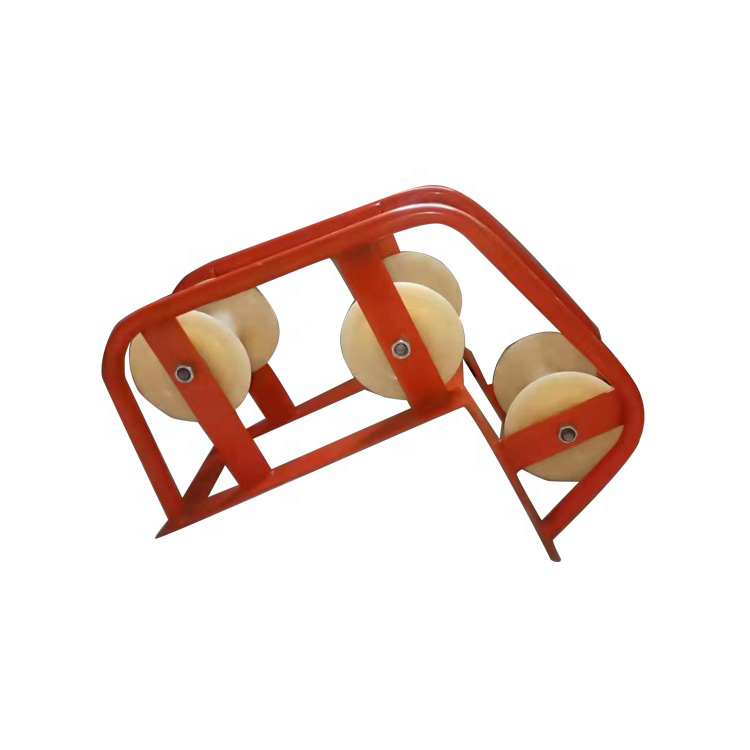


Understanding the Role of a Cable Laying Roller
A Cable Laying Roller supports cables during installation by reducing direct contact with the ground or structural edges. It allows the cable to move freely while maintaining alignment along the intended route.
In professional installation environments, cable laying rollers are considered standard equipment for minimizing pulling force and preventing mechanical damage during cable deployment.
Differences Between Single and Multi-Cable Projects
Before setting up rollers, it is important to understand the differences between single-cable and multi-cable installations.
·Single-cable projects typically involve larger, heavier cables with higher individual tension.
·Multi-cable projects involve multiple smaller cables laid simultaneously, increasing complexity in spacing and alignment.
Each scenario requires a tailored roller setup strategy to ensure smooth and controlled cable movement.
Planning the Cable Route Layout
Proper planning is the foundation of effective roller setup. The cable route should be inspected for straight sections, bends, elevation changes, and obstacles.
Key planning considerations include:
·Total route length
·Cable diameter and weight
·Number of directional changes
·Installation environment (trench, surface, or tunnel)
Accurate route planning helps determine roller type, quantity, and placement intervals.
Roller Spacing Guidelines for Single-Cable Projects
In single-cable installations, roller spacing focuses on supporting cable weight evenly and reducing sag.
General setup principles include:
·Closer spacing for heavier or stiffer cables
·Additional rollers at bends and transitions
·Stable positioning on uneven ground
Proper spacing ensures that tension is distributed consistently throughout the cable length.
Roller Arrangement for Multi-Cable Projects
Multi-cable projects require careful coordination to prevent cables from crossing, twisting, or rubbing against each other.
Recommended practices include:
·Using multi-channel or guide rollers where applicable
·Maintaining consistent spacing between cables
·Ensuring synchronized cable feeding
A well-organized roller layout improves installation efficiency and reduces the risk of surface damage.
Handling Bends, Corners, and Elevation Changes
Bends and elevation changes are high-risk areas for cable damage. Cable laying rollers should be positioned precisely to guide cables smoothly through these sections.
For corners, angled or corner rollers help maintain proper alignment. For elevation changes, additional rollers reduce localized stress and prevent sudden tension increases.
Careful setup in these areas significantly improves overall installation control.
Ensuring Stability and Alignment
Roller stability is critical during cable laying. Unstable rollers can shift under load, causing misalignment or sudden cable movement.
Best practices include:
·Securing rollers on firm ground
·Verifying alignment before pulling begins
·Conducting a test run with minimal tension
Stable and aligned rollers create a predictable cable path and improve safety.
Safety Considerations During Roller Setup
Safety should be prioritized throughout the setup process. Installation teams should ensure that rollers are positioned clear of walkways and that cables remain under controlled tension.
Clear communication among team members helps prevent accidents during pulling operations. Proper setup reduces sudden movements that could pose risks to personnel.
Role of Cable Laying Rollers in Large-Scale Projects
In large infrastructure projects, consistent roller setup supports efficient workflows. From a manufacturer perspective, standardized roller designs allow reliable performance across various installation scenarios.
During production, durability testing ensures that cable laying rollers can withstand repeated use in demanding environments, making them suitable for long-term and bulk supply deployment.
Maintenance and Reuse of Cable Laying Rollers
After installation, rollers should be inspected for wear or damage. Bearings should rotate freely, and frames should remain structurally sound.
Routine inspection and basic maintenance help extend roller service life and ensure consistent performance across multiple projects.
Common Setup Mistakes to Avoid
Even experienced teams can encounter issues if setup is rushed. Common mistakes include:
·Excessive roller spacing
·Poor alignment at bends
·Ignoring ground stability
Avoiding these errors improves installation quality and reduces rework.
Conclusion: Optimizing Cable Installation with Proper Roller Setup
A well-planned Cable Laying Roller setup is essential for both single and multi-cable projects. By carefully planning the route, selecting appropriate roller spacing, and ensuring stability, installation teams can significantly improve efficiency and cable protection.
Proper roller setup supports safer operations, reduces mechanical stress, and contributes to reliable cable performance across a wide range of industrial and infrastructure applications.
References
GB/T 7714:Anders G J. Rating of electric power cables: ampacity computations for transmission, distribution, and industrial applications[J]. (No Title), 1997.
MLA:Anders, George J. "Rating of electric power cables: ampacity computations for transmission, distribution, and industrial applications." (No Title) (1997).
APA:Anders, G. J. (1997). Rating of electric power cables: ampacity computations for transmission, distribution, and industrial applications. (No Title).