Heavy-Duty Cable Rollers for High-Tension Cable Routes
Author:jiujiu Release time:2026-01-09 16:11:49 Number of views:180order
Challenges of High-Tension Cable Installation
Installing cables along high-tension routes presents unique challenges. These routes often involve long distances, heavy cable weight, sharp directional changes, and strict safety requirements. Without proper guidance and support, cables can suffer damage, excessive friction, or misalignment during installation.
A Cable Roller is a critical accessory designed to guide cables smoothly along predefined paths. In high-tension applications, heavy-duty cable rollers play a vital role in maintaining cable integrity, reducing pulling force, and improving overall installation efficiency.
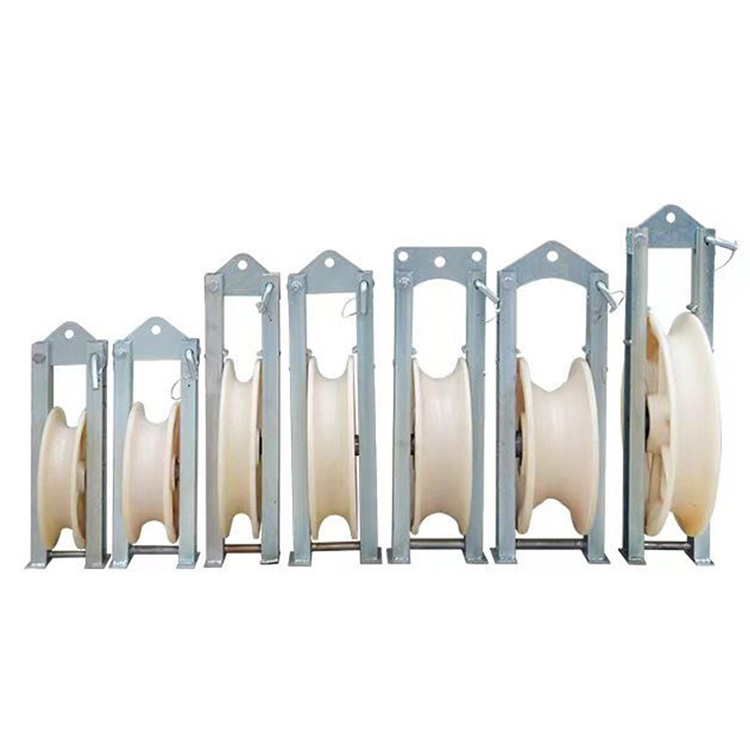
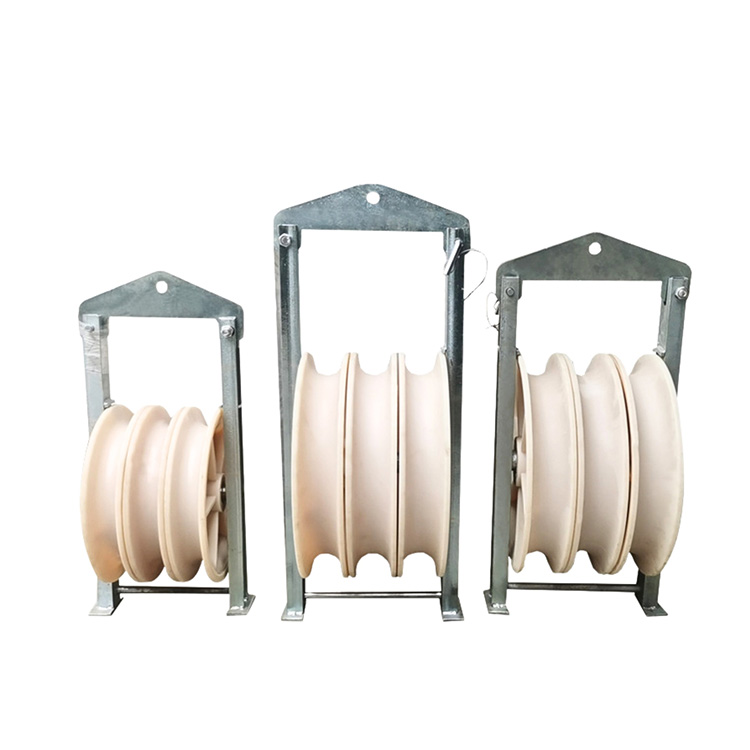


What Is a Heavy-Duty Cable Roller?
A heavy-duty Cable Roller is a mechanical device used to support and guide power cables, communication cables, or industrial lines during pulling and laying operations. Compared to standard rollers, heavy-duty designs are engineered to handle higher loads, increased tension, and harsh working conditions.
These rollers typically feature reinforced frames, high-load bearings, and durable roller surfaces that allow cables to move freely while remaining properly aligned.
Importance of Cable Rollers in High-Tension Routes
High-tension cable routes often involve elevated stress levels due to cable weight and pulling force. Without adequate support, friction between the cable and ground or conduit edges can cause surface abrasion or internal damage.
Using heavy-duty cable rollers helps:
·Minimize friction during cable pulling
·Maintain consistent cable alignment
·Prevent sheath damage
·Reduce installation force and labor strain
By distributing the load evenly, cable rollers ensure safer and more controlled cable handling.
Common Applications of Heavy-Duty Cable Rollers
Heavy-duty cable rollers are widely used in infrastructure and industrial projects where high-tension cable installation is required. Typical applications include:
·Power transmission and distribution projects
·Industrial plants and refineries
·Tunnel and trench cable routing
·Substation and utility installations
In these environments, reliability and load capacity are essential, making robust cable roller designs a practical necessity.
Structural Features Designed for Heavy Loads
The performance of a Cable Roller depends largely on its structural design. Heavy-duty models are built to withstand continuous use under significant tension.
Key structural features include:
·High-strength steel frames for load stability
·Precision bearings for smooth rotation
·Wear-resistant roller materials
·Reinforced axles and mounting points
These design elements help maintain consistent performance even under demanding installation conditions.
Reducing Cable Damage and Installation Risks
Cable damage during installation can lead to costly repairs, signal loss, or premature system failure. Heavy-duty cable rollers reduce direct contact between the cable and rough surfaces, minimizing abrasion and deformation.
Additionally, controlled cable movement reduces sudden tension spikes, improving safety for installation crews. This is especially important in long-distance or high-elevation cable routes where tension levels fluctuate.
Role in Efficient Project Execution
Efficiency is a major concern in large-scale cable installation projects. Heavy-duty cable rollers contribute to faster setup and smoother cable movement, reducing downtime and manual intervention.
From a manufacturer perspective, standardized cable roller designs support consistent performance across multiple projects. During production, durability testing ensures rollers can meet load requirements for high-tension applications.
Choosing the Right Cable Roller for High-Tension Routes
Selecting the correct cable roller involves evaluating several factors:
·Maximum cable diameter and weight
·Expected pulling tension
·Route layout and directional changes
·Environmental conditions
Rollers should be positioned strategically along straight runs, bends, and elevation changes to ensure continuous support throughout the cable route.
Maintenance and Long-Term Reliability
Heavy-duty cable rollers are designed for repeated use, but regular inspection is essential to maintain performance. Bearings should rotate freely, frames should remain structurally sound, and roller surfaces should be free from excessive wear.
Routine maintenance helps extend service life and ensures consistent performance, especially in projects involving bulk supply and repeated installations.
Comparison with Light-Duty Cable Rollers
While light-duty rollers may be suitable for smaller cables or short runs, they often lack the strength required for high-tension routes. Heavy-duty cable rollers offer higher load capacity, greater stability, and improved durability.
For large infrastructure projects, using appropriately rated rollers reduces the risk of equipment failure and improves overall installation quality.
Safety Considerations During Installation
Safety is a critical factor when working with high-tension cables. Properly placed cable rollers help control cable movement, reducing the risk of sudden shifts or uncontrolled release of tension.
Installation teams should follow recommended spacing and alignment practices to ensure rollers function as intended throughout the pulling process.
Conclusion: Supporting High-Tension Cable Routes with Confidence
Heavy-duty Cable Rollers are essential tools for managing high-tension cable routes efficiently and safely. By reducing friction, protecting cable surfaces, and improving control during installation, they contribute directly to project reliability and performance.
When selected and maintained correctly, cable rollers become a dependable component in demanding cable installation environments, supporting consistent results across a wide range of industrial and infrastructure applications.
References
GB/T 7714:Anders G J. Rating of electric power cables: ampacity computations for transmission, distribution, and industrial applications[J]. (No Title), 1997.
MLA:Anders, George J. "Rating of electric power cables: ampacity computations for transmission, distribution, and industrial applications." (No Title) (1997).
APA:Anders, G. J. (1997). Rating of electric power cables: ampacity computations for transmission, distribution, and industrial applications. (No Title).